What Is ERV in HVAC?
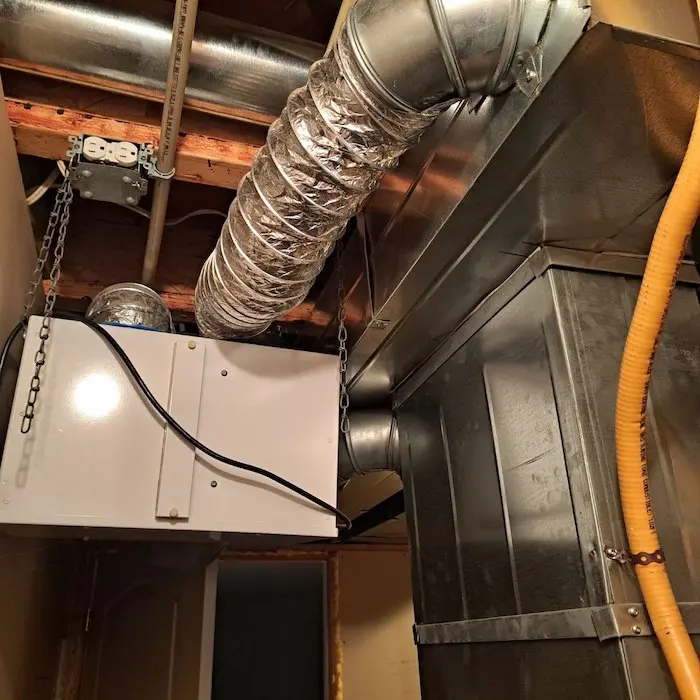

Defining ERV in the HVAC Context
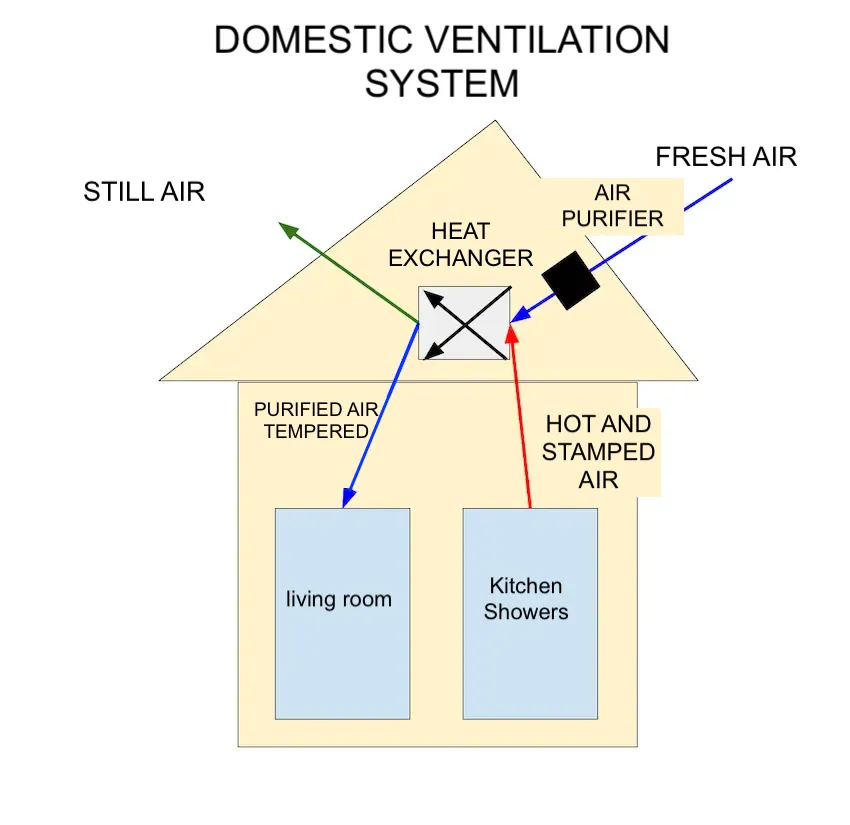
What is ERV in HVAC? An energy recovery ventilator (ERV) is a ventilation system integrated into HVAC setups that exchanges stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air while transferring heat and moisture to enhance energy efficiency.
An energy recovery ventilator reduces the energy needed to condition incoming air, making it a key component in modern home HVAC systems for homes and commercial buildings.
By improving indoor air quality and minimizing energy loss, an ERV in HVAC is ideal for tightly sealed structures where natural ventilation is limited.
Why Is an ERV Important in HVAC Systems?

An energy recovery ventilator helps maintain healthy indoor air by reducing pollutants, allergens, and excess humidity, which is critical for occupant health in energy-efficient buildings.
In HVAC applications, an ERV lowers utility costs by recovering up to 85% of the heat and moisture from outgoing air, reducing the workload on heating and cooling systems.
With building codes increasingly requiring ventilation, an energy recovery ventilator ensures compliance while supporting sustainability goals in modern HVAC designs.
What Is an Energy Recovery Ventilator?
Core Functionality of an ERV
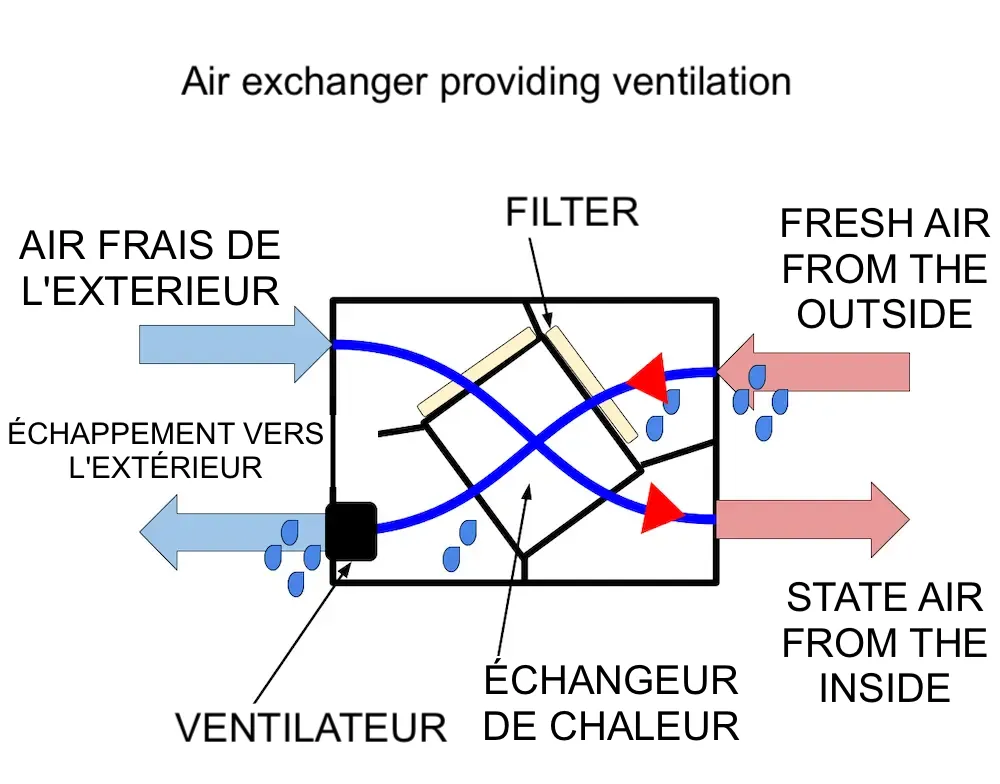
What is an energy recovery ventilator? An ERV is a device that ventilates buildings by exchanging air while transferring both heat and moisture, optimizing energy use and indoor comfort.
The enthalpy wheel or membrane in an energy recovery ventilator facilitates the transfer of heat and humidity between air streams, preventing energy waste during ventilation.
An energy recovery ventilator is particularly effective in humid climates, where it controls moisture to prevent mold growth and maintain comfortable indoor conditions.
Components of an ERV
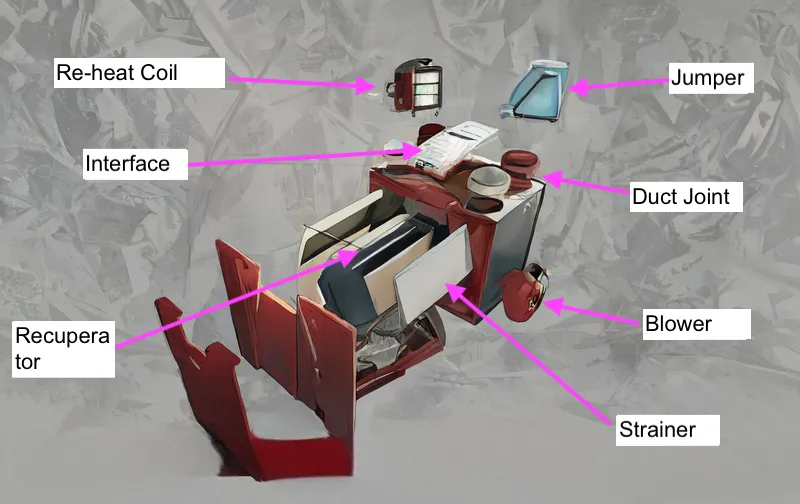
The core of an energy recovery ventilator, typically an enthalpy wheel or cross-flow membrane, transfers heat and moisture without mixing incoming and outgoing air streams.
Dual fans in an ERV ensure balanced airflow, drawing in fresh air and expelling stale air through separate ducts for continuous ventilation.
High-efficiency filters in an energy recovery ventilator capture dust, pollen, and other particles, protecting the system and improving indoor air quality.
- Choose an energy recovery ventilator with a high sensible recovery efficiency (SRE) of 80% or more for optimal performance.
- Ensure the ERV has HEPA or MERV 13 filters for allergy-prone households.
- Opt for models with quiet operation, ideally below 1.5 sones, to minimize noise.
- Verify ENERGY STAR certification for rebates on your ERV in HVAC system.
- Schedule regular maintenance to keep the enthalpy core of the energy recovery ventilator clean and efficient.
What Is Energy Recovery Ventilation?
The Process of Energy Recovery Ventilation
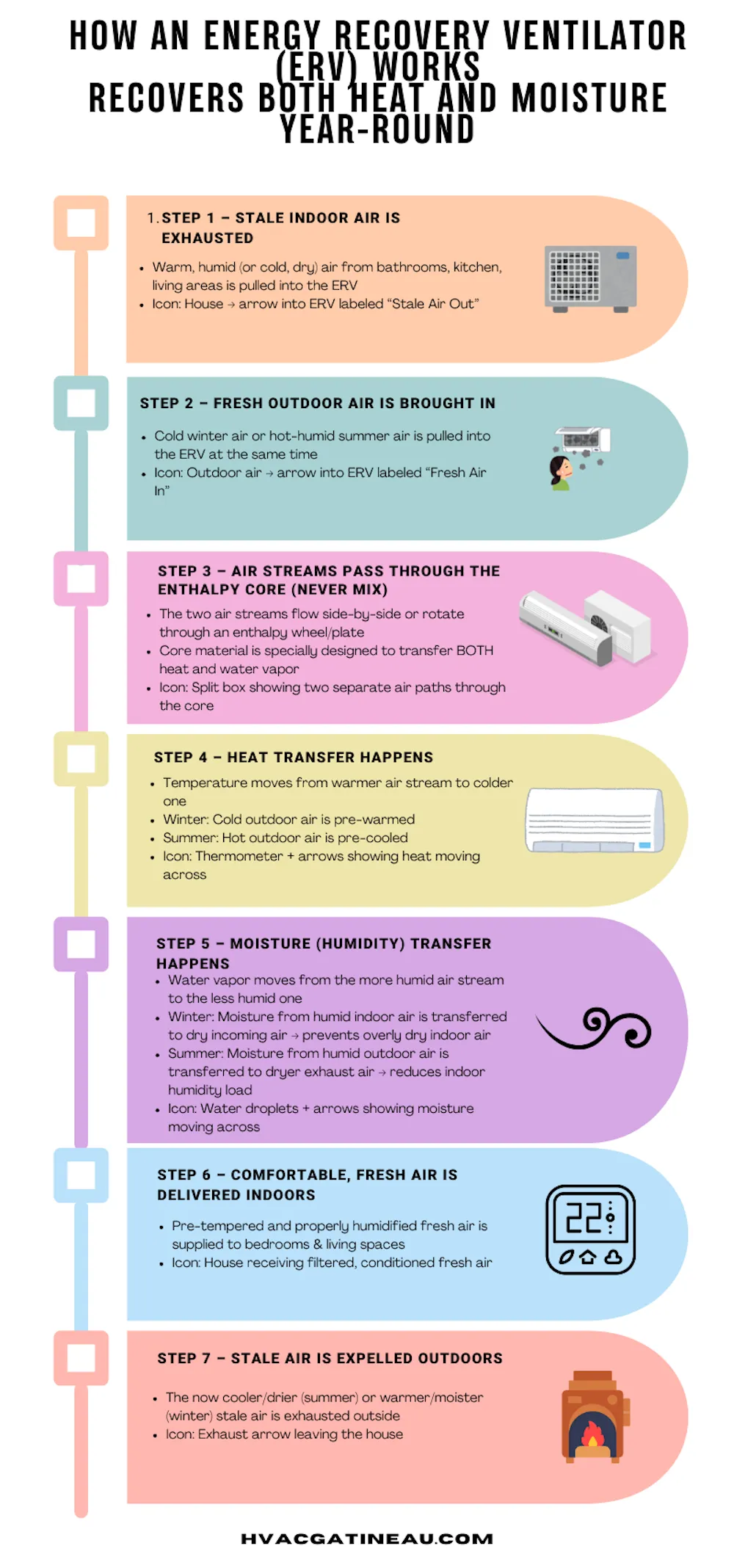
What is energy recovery ventilation? It’s the process of exchanging indoor and outdoor air while transferring heat and moisture to reduce energy loss and control humidity levels.
An energy recovery ventilator uses its core to precondition incoming air, reducing the energy needed to heat or cool it, thus lowering HVAC operational costs.
By managing humidity, energy recovery ventilation prevents issues like mold or overly dry air, enhancing comfort in diverse climates like humid summers or dry winters.
Benefits of Energy Recovery Ventilation

An energy recovery ventilator improves indoor air quality by reducing CO2, VOCs, and allergens, creating a healthier environment for occupants with respiratory sensitivities.
With energy recovery rates up to 90%, an ERV in HVAC systems can save 15-20% on heating and cooling costs compared to traditional ventilation methods.
The humidity control of an energy recovery ventilator is ideal for preventing condensation in tightly sealed homes, especially in humid regions.
What Is a Heat Recovery Ventilator?
Comparing ERV and HRV
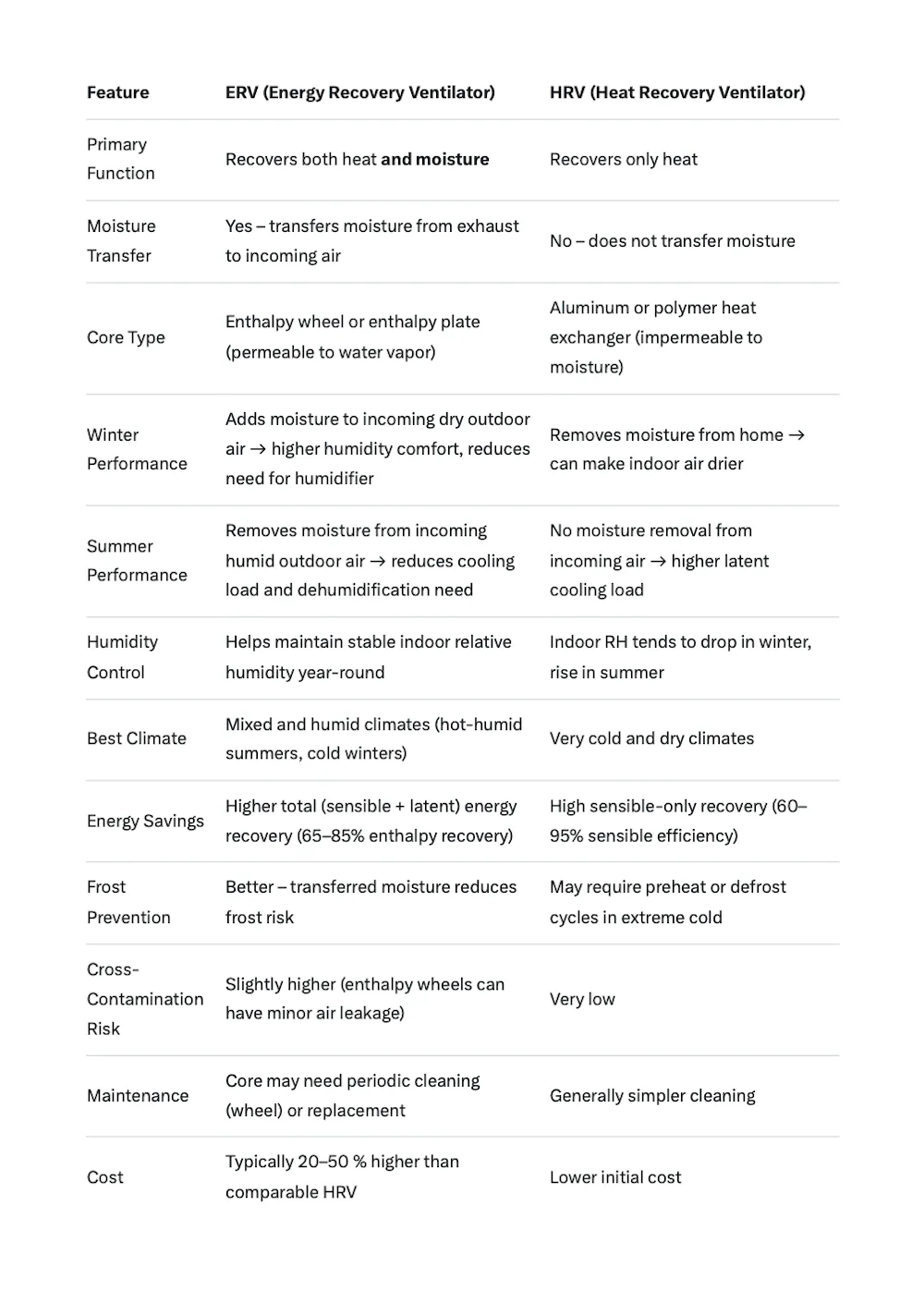
What is a heat recovery ventilator? An HRV transfers only heat between air streams, unlike an energy recovery ventilator, which also manages moisture, making HRVs better for dry climates.
An HRV is suited for cold, dry regions like much of Canada, where humidity control is less critical, while an energy recovery ventilator excels in humid environments.
Choosing between an HRV and an ERV in HVAC depends on your climate and humidity needs, with ERVs offering more comprehensive moisture management.
What Does a Heat Recovery Ventilator Do?

What does a heat recovery ventilator do? It exchanges stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air, transferring heat to reduce energy loss, ideal for cold climates.
Unlike an energy recovery ventilator, an HRV does not transfer moisture, which can lead to drier indoor air in winter but simplifies operation in cold regions.
An HRV reduces heating costs by recovering heat from outgoing air, making it a cost-effective complement to an ERV in HVAC systems for specific climates.
What Is a ERV?
Understanding the ERV Concept
What is a ERV? It’s a ventilation system that recovers both heat and moisture, balancing air quality and energy efficiency in residential or commercial settings.
An energy recovery ventilator is particularly valuable in humid climates, preventing mold and maintaining comfortable indoor humidity levels between 30-50%.
In modern HVAC systems, an ERV supports sustainability by reducing energy consumption while ensuring fresh air, meeting stringent building ventilation codes.
Applications of ERVs in HVAC
Residential Applications
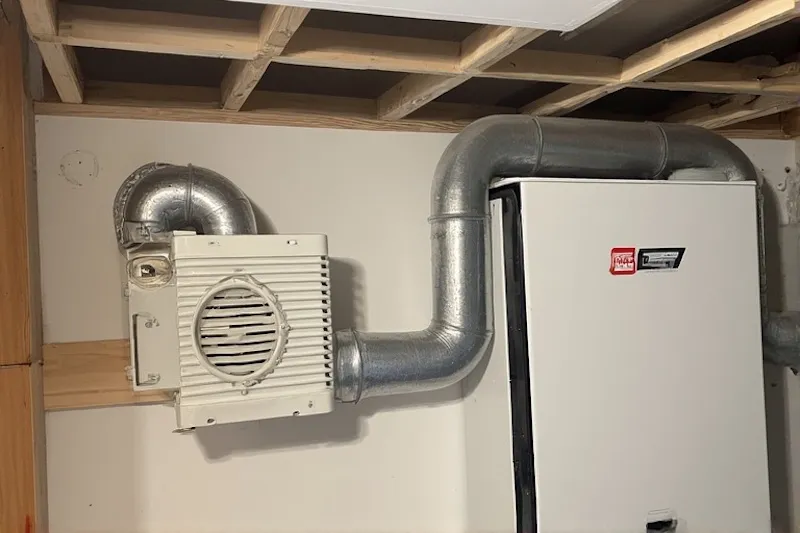

An energy recovery ventilator is ideal for energy-efficient homes, where tight sealing limits natural ventilation, preventing stale air buildup and improving health.
For allergy-prone households, an ERV in HVAC systems with HEPA filters removes fine particles, enhancing air quality and reducing respiratory issues.
In Quebec’s humid summers and dry winters, an energy recovery ventilator balances ventilation and humidity, ensuring year-round comfort in homes.
Commercial and Industrial Applications

In offices, an energy recovery ventilator provides fresh air to employees, reducing sick building syndrome while lowering HVAC energy costs in large spaces.
Restaurants and gyms rely on an ERV in HVAC systems to manage high humidity and odors, maintaining a pleasant environment without excessive energy use.
Industrial facilities use an energy recovery ventilator to meet ventilation standards while recovering energy, supporting sustainability in high-occupancy spaces.
Choosing the Best ERV for HVAC
Top ERV Models and Brands

The Panasonic Intelli-Balance 100, a top energy recovery ventilator, offers up to 93% heat recovery efficiency and quiet operation at 0.8 sones, ideal for homes.
Venmar’s AVS E15, a leading ERV in HVAC, features durable enthalpy cores and smart controls, perfect for cold and humid climates like Canada.
Fantech’s SER series, another high-performing energy recovery ventilator, excels in humidity control, making it a top choice for coastal or humid regions.
Selection Criteria
Select an energy recovery ventilator with a capacity (50-200 CFM) suited to your building’s size to ensure effective ventilation without overloading the system.
Look for an ERV in HVAC with high sensible and latent recovery efficiencies (above 80%) and low noise levels for optimal comfort and performance.
Choose an energy recovery ventilator with a warranty of at least 5 years on the core and 2 years on parts to protect your investment.
Installation and Maintenance
Professional Installation
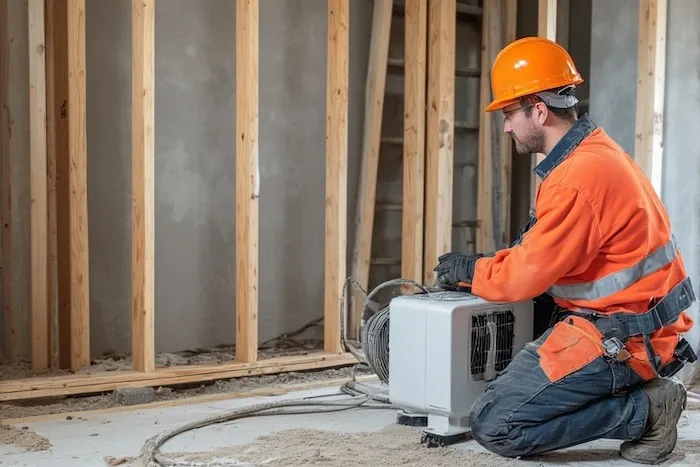

Installing an energy recovery ventilator requires a professional certified technician to ensure proper ductwork, balanced airflow, and compliance with local building codes.
Improper installation of an ERV in HVAC can lead to air leaks or reduced efficiency, increasing energy costs and compromising air quality.
Installation costs for an energy recovery ventilator range from $2,000 to $5,000, depending on the building’s size and ductwork complexity.
Maintenance Requirements
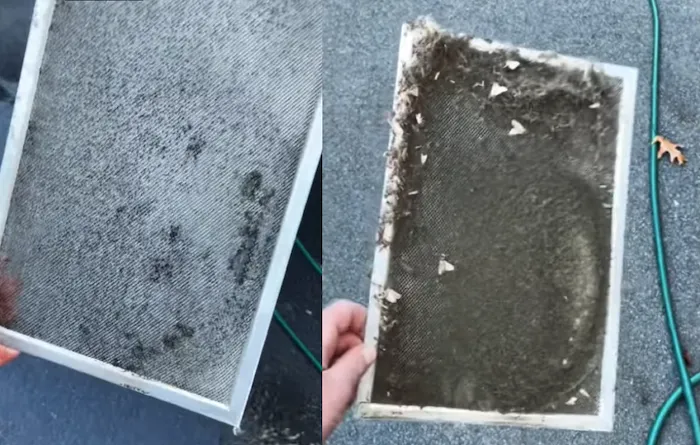

Clean or replace the filters of an energy recovery ventilator every 3-6 months to maintain airflow and prevent dust buildup, ensuring optimal performance.
Inspect the enthalpy core of an ERV annually, cleaning it with mild soap to remove debris and maintain heat and moisture transfer efficiency.
Schedule professional maintenance for an energy recovery ventilator every 2-3 years to check fans, ducts, and controls, costing $100-$200 per visit.
Performance in Different Climates
Operation in Humid Climates
An energy recovery ventilator excels in humid climates, transferring moisture to prevent mold and maintain comfortable indoor humidity levels.
In summer, an ERV in HVAC systems reduces the humidity of incoming air, easing the load on air conditioners and improving energy efficiency.
Models like Fantech’s SER series optimize energy recovery ventilation in coastal areas, ensuring consistent performance in high-humidity environments.
Operation in Cold Climates
In winter, an energy recovery ventilator prevents excessive humidity buildup in sealed homes, reducing mold risk while recovering heat for energy savings.
Some ERVs include preheaters to prevent core freezing in sub-zero temperatures, ensuring reliable operation in harsh winters.
An energy recovery ventilator maintains indoor humidity at 30-50% in cold climates, avoiding overly dry air that can cause discomfort.
Cost and Incentives
Cost of an Energy Recovery Ventilator
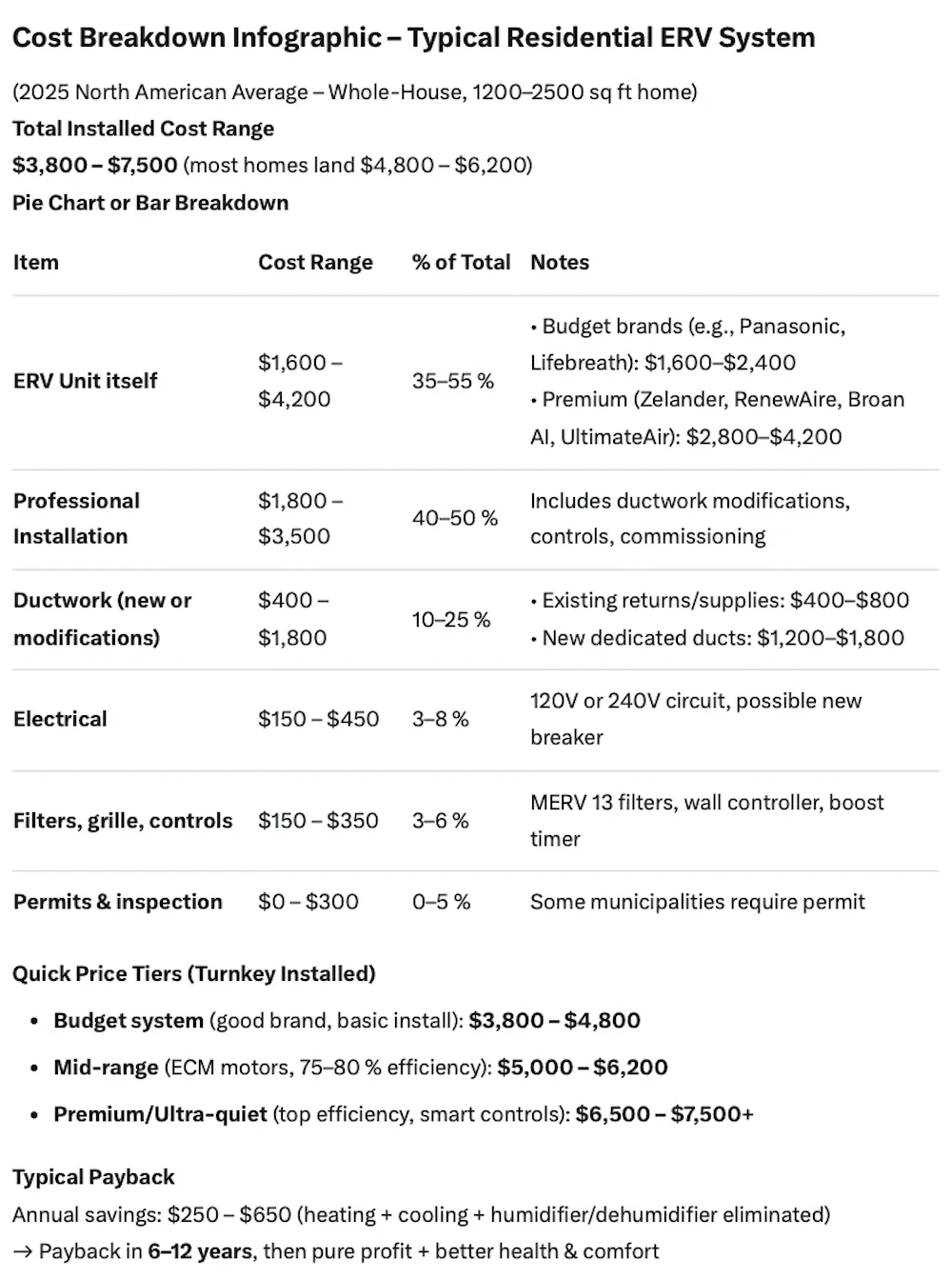
An energy recovery ventilator costs $1,500-$4,000 for the unit, with installation fees of $2,000-$5,000 depending on system complexity and ductwork.
High-efficiency models like Panasonic’s Intelli-Balance reduce energy costs, offering a return on investment within 5-7 years for an ERV in HVAC.
Maintenance costs for an energy recovery ventilator are minimal, typically $100-$200 annually for filter replacements and professional servicing.
Available Incentives
In Canada, Hydro-Quebec offers rebates up to $1,000 for an ENERGY STAR-certified energy recovery ventilator, lowering upfront costs.
In the U.S., federal tax credits through 2025 cover 30% of the cost of an ERV in HVAC, up to $600, under the Inflation Reduction Act.
Local utility programs may provide additional incentives for an energy recovery ventilator, so check with your provider to maximize savings.
Conclusion: The Value of an ERV in HVAC
Why Choose an ERV?
Understanding what is an ERV in HVAC highlights its role in enhancing air quality, reducing energy costs, and controlling humidity in modern buildings.
An energy recovery ventilator is a smart investment for homes and businesses, offering health benefits, comfort, and sustainability in one system.
By selecting a high-quality ERV and maintaining it properly, you ensure a healthier, more efficient indoor environment for years to come.
Maximize Your Home's Comfort with Gatineau's HVAC Expert
Unlock the full potential of your home's climate control. Expert installation and diligent maintenance of your
HVAC system are the most effective ways to enhance comfort, reduce energy costs, and prevent
unexpected breakdowns.
For Gatineau homeowners seeking this advantage, HVAC Gatineau delivers. Start the conversation today by calling +1 (819) 485-0516 or emailing hvacgatineau@outlook.com.
From system upgrades to precision tune-ups, they provide tailored solutions. Taking the first step is easy—secure your preferred appointment time through their digital scheduling platform. For a complete overview of their benefits and to obtain a no-obligation quote, visit their website: hvacgatineau.com.
Further reading
- What Is an Energy Recovery Ventilator?
- What Is a Ductless Heat Pump?
- What Is a Heat Recovery Ventilator?
- Where Can I Buy Water Heaters?
Need Professional Help?
If your ERV system in your HVAC setup is not ventilating properly or seems inefficient, our certified technicians are ready to diagnose and resolve the problem. Discover our air exchanger installation, repair, and maintenance services in Gatineau.
Approved sites
Breaking Down ERVs in HVAC for Healthier Indoor Air +1 (819) 485 0516
What Is ERV in HVAC?

Nous offrons des services complets de CVC à Gatineau, Québec, spécialisés dans le chauffage, la climatisation, les thermopompes et les échangeurs d’air pour des projets résidentiels et commerciaux. hvacgatineau@outlook.com


Contactez-nous
HVAC Gatineau Services de Chauffage, Climatisation et Ventilation
Si vous recherchez des solutions CVC de qualité près de chez vous, notre équipe d’experts chez HVAC Gatineau vous garantit des résultats durables pour l’installation, la réparation et l’entretien de systèmes de chauffage, climatisation, thermopompes et échangeurs d’air. Nous servons Gatineau, Hull, Aylmer, Buckingham, Masson-Angers et les environs. Contactez-nous pour un devis rapide sur vos besoins en CVC à Gatineau et dans les environs.

